Table des matières
Esp32 est un microcontrôleur qui va nous permettre de faire des objets connectés grâce a son module Wifi et Bluetooth intégré. Il dispose de plusieurs sorties et entrées pour connecter par exemple des capteurs ou des LED.
On va utiliser Micropython pour assurer la programmation.
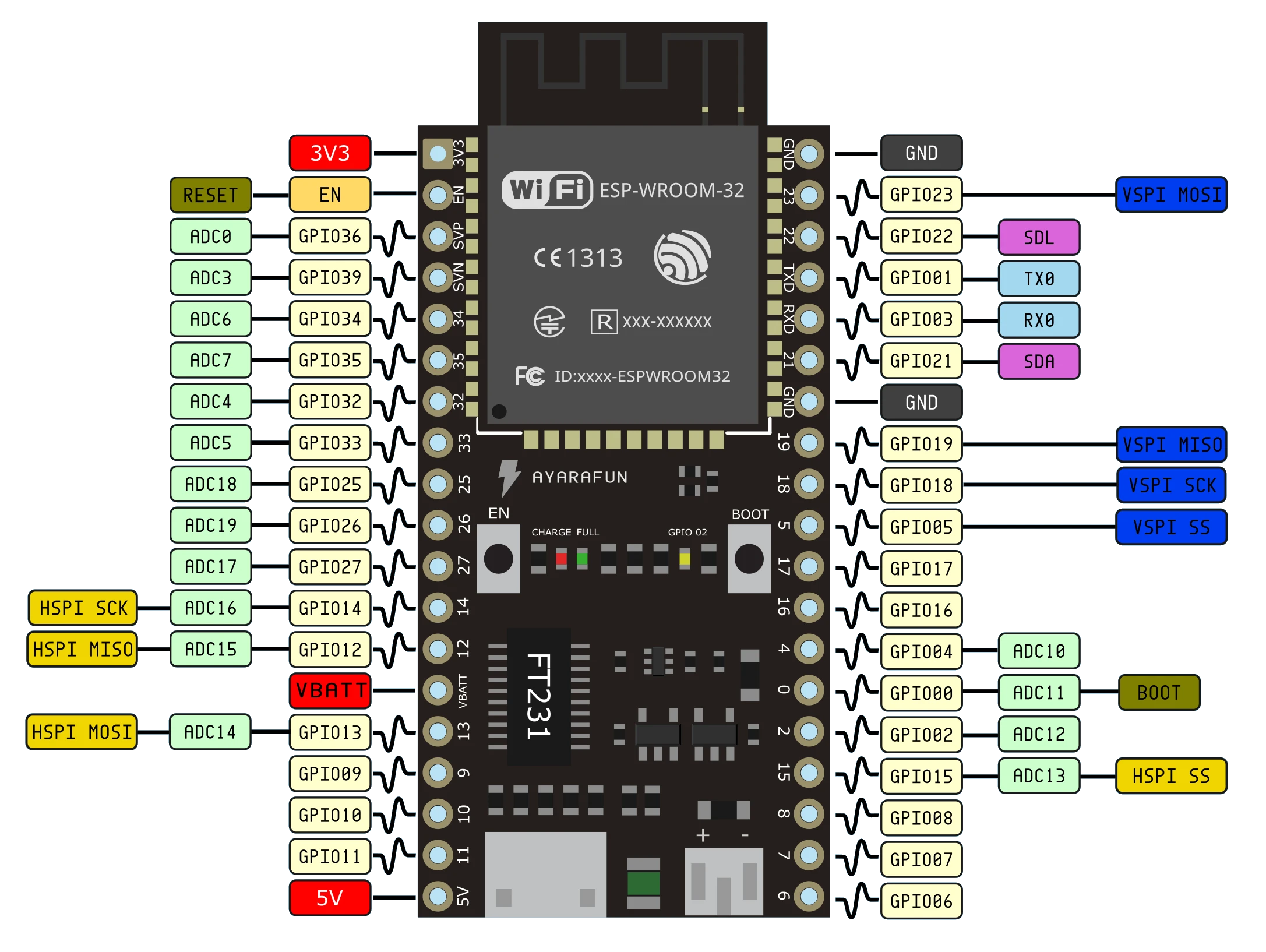
Dans un premier temps, il faut changer le logiciel a l’intérieur pour installer MicroPython.
Installation esptool
$ apt install esptoolOn branche l’esp32 et on lance un dmesg pour savoir ou il se trouve sur les ports.
$ dmesg
cp210x converter now attached to ttyUSB0Installation MicroPython
Effacement complet de la carte avec esptool.
$ esptool --port /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash
esptool.py v2.8
Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0
Connecting........___
Detecting chip type... ESP32
Chip is ESP32D0WDQ6 (revision 1)
Features: WiFi, BT, Dual Core, Coding Scheme None
Crystal is 40MHz
MAC: 30:ae:a4:26:d2:00
Enabling default SPI flash mode...
Erasing flash (this may take a while)...
A fatal error occurred: ESP32 ROM does not support function erase_flash.ARF ça ne marche pas, faut une version plus récente d’esptool.
$ git clone https://github.com/espressif/esptool.git
$ cd esptool
$ python3 esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash
esptool.py v4.7-dev
Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0
Connecting.....
Chip is ESP32-D0WDQ6 (revision v1.0)
Features: WiFi, BT, Dual Core, Coding Scheme None
Crystal is 40MHz
MAC: 30:ae:a4:26:d2:00
Uploading stub...
Running stub...
Stub running...
Erasing flash (this may take a while)...
Chip erase completed successfully in 4.4
Hard resetting via RTS pin...Recuperation du microcode sur le site de MicroPython.
$ wget https://micropython.org/resources/firmware/esp32-20230426-v1.20.0.binOn injecte le microcode.
$ python3 esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --baud 460800 write_flash 0x1000 esp32-20230426-v1.20.0.bin
esptool.py v4.7-dev
Serial port /dev/ttyUSB0
Connecting......
Chip is ESP32-D0WDQ6 (revision v1.0)
Features: WiFi, BT, Dual Core, Coding Scheme None
Crystal is 40MHz
MAC: 30:ae:a4:26:d2:00
Uploading stub...
Running stub...
Stub running...
Changing baud rate to 460800
Changed.
Configuring flash size...
Flash will be erased from 0x00001000 to 0x0017ffff...
Compressed 1566528 bytes to 1034676...
Wrote 1566528 bytes (1034676 compressed) at 0x00001000 in 23.5 seconds (effective 532.2 kbit/s)...
Hash of data verified.
Leaving...
Hard resetting via RTS pin...Connection a l’Esp32
On va utiliser picocom pour se connecter.
$ sudo apt install picocom$ picocom /dev/ttyUSB0 -b115200
picocom v3.1
port is : /dev/ttyUSB0
flowcontrol : none
baudrate is : 115200
parity is : none
databits are : 8
stopbits are : 1
escape is : C-a
local echo is : no
noinit is : no
noreset is : no
hangup is : no
nolock is : no
send_cmd is : sz -vv
receive_cmd is : rz -vv -E
imap is :
omap is :
emap is : crcrlf,delbs,
logfile is : none
initstring : none
exit_after is : not set
exit is : no
Type [C-a] [C-h] to see available commands
Terminal ready
>>> print('hello esp8266!')
hello esp8266!
>>> 1+2
3Liens
Métadonnées
Posté le: 05.09.2023
Nombre de mots: 457
Temps de lecture: 3 minutes
Cet article fait partie de la série: Esp32
Latex de la couleur dans vos codes Convertir de Markdown vers Pdf